Understanding Ethernet Cables: A Comprehensive Guide
Contact for Free Quotation & Sample, According to your needs, customize for you.
inquiry nowUnderstanding Ethernet Cables: A Comprehensive Guide
In the digital age, connectivity is key. The backbone of this connectivity is often an overlooked component: the Ethernet cable.
Ethernet cables are the lifelines of our local area networks (LANs). They connect our devices, enabling communication and data transfer.
But what exactly is an Ethernet cable?
This guide will delve into the world of Ethernet cables. We'll explore their structure, types, and categories, and how they've evolved over time.
We'll also discuss their role in network performance. From bandwidth and data speed to cable shielding and standards, we'll cover it all.
Whether you're a tech enthusiast, an IT professional, or a home user setting up a network, this guide is for you.
Join us as we unravel the intricacies of Ethernet cables, helping you make informed decisions for your networking needs.

What is an Ethernet Cable?
Ethernet cables are an essential component of computer networking. They serve as the physical medium for connecting devices within a network.
Primarily, Ethernet cables link computers, routers, and switches in a local area network (LAN). This enables fast and reliable data transfer.
These cables are typically made of copper wires. They come encased in protective jackets, ensuring signal integrity during transmission.
Ethernet cables have become ubiquitous in both homes and businesses. Their design allows for effective communication over short to medium distances.
Key functions of Ethernet cables include:
- Enabling data communication between devices
- Supporting high-speed internet connections
- Facilitating network device management
Over the years, Ethernet cables have evolved with technology advances. This evolution has led to improvements in speed and performance.
Overall, Ethernet cables are vital for maintaining robust networks. Their role is to keep our digital world interconnected and functioning efficiently.
The Evolution of Ethernet Cables
Ethernet cables have experienced significant evolution since their inception. Initially developed in the 1970s, Ethernet was created to meet the growing needs for local area network (LAN) connections.
The journey began with coaxial cables that provided limited speeds and capabilities. Over time, these were replaced by more versatile twisted-pair cables, which improved connectivity and reliability.
Today, we have advanced to categories like Cat5, Cat6, and beyond. Each iteration boasts higher speeds, bandwidth, and durability. This evolution reflects the constant demand for faster internet and enhanced data transfer capabilities.
Ethernet cables have thus consistently adapted to the demands of modern technology. They continue to play a crucial role in supporting the ever-expanding digital world. As future technologies emerge, Ethernet cables are expected to continue evolving, ensuring they meet emerging networking needs.
Ethernet Cable Structure and Twisted Pair Significance
Ethernet cables are made up of twisted pairs of copper wires. This unique structure is central to their design. Each pair of wires twists around each other to cancel out interference.
The twisting helps to minimize electromagnetic interference from external sources. This ensures a stable and reliable data transmission. These cables usually contain four pairs of twisted wires inside a protective jacket.
Twisted pair cables come in two main types: Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Shielded Twisted Pair (STP). The key difference lies in their protection from interference. UTPs are more common and sufficient for most home and office networks.
This design choice contributes significantly to reducing signal degradation over longer distances. The careful engineering of these twisted pairs has been essential in achieving high-speed data transfers. The result is enhanced network performance, which is essential for smooth connectivity.
Overall, the twisted pair structure is a cornerstone of Ethernet cable technology. It offers practical benefits in reducing interference and maintaining signal integrity.
Ethernet Cable Categories and Types
Ethernet cables are categorized based on their performance characteristics. Different categories offer varying levels of speed, bandwidth, and shielding. Selecting the right category can significantly impact network efficiency.
The categories range from Cat5 to the latest Cat8. As the category number rises, so do potential speed and bandwidth. Higher categories often support faster data rates and more demanding applications.
Here's a breakdown of common Ethernet cable categories:
- Cat5 and Cat5e: Basic speed and reliability for everyday needs.
- Cat6 and Cat6a: Enhanced speeds with reduced crosstalk, ideal for gigabit networks.
- Cat7 and Cat8: High-performance needs, ideal for data centers.
Ethernet cables are crucial in any networking setup. Their capability influences data flow and overall network performance. Each category serves different environments, from small offices to large data centers.
Choosing the right category requires understanding specific network requirements. Factors to consider include network size, device speed, and future needs. It's important to balance cost with performance.
In essence, understanding these categories helps in crafting a robust network. Proper selection can lead to improved efficiency and reduced latency. By staying informed, you can ensure your network operates at peak performance.
Category 5 (Cat5) and Category 5e (Cat5e)
Cat5 cables were the standard for many years. They support speeds up to 100 Mbps, making them suitable for basic internet use. However, they may fall short for modern applications.
Cat5e emerged as an improved version. It supports gigabit speeds and reduces interference. For homes and small businesses, Cat5e remains a reliable choice. This category offers a cost-effective solution without sacrificing too much performance.
Category 6 (Cat6) and Category 6a (Cat6a)
Cat6 cables provide a significant upgrade over Cat5e. They handle up to 10 Gigabit speeds over short distances. This makes them ideal for high-speed connections in offices and businesses.
Cat6a further increases this capability. It offers 10 Gigabit support over longer distances with reduced crosstalk. This makes it suitable for server rooms and heavier data needs. Cat6a offers future-proofing for expanding networks.
Category 7 (Cat7) and Category 8 (Cat8)
Cat7 cables take performance a step further. With shielded pairs, they reduce interference even more effectively. They handle speeds up to 10 Gigabit and are designed for high-speed networking environments.
Cat8 is the peak of Ethernet technology. It supports speeds up to 25 or even 40 Gigabit over short lengths. This is especially beneficial for data centers and network backbones. Cat8 represents the cutting edge of Ethernet capability.
Understanding RJ45 Connectors
RJ45 connectors are crucial in Ethernet cabling. They are the standard connectors used for network cables. Each RJ45 comprises eight pins that align with the cable's wires. This ensures reliable data transmission and connectivity. The connector's design focuses on maintaining a stable electrical connection.
The RJ45 connector fits snugly into an Ethernet port. This design minimizes potential signal loss. It is universally used, making it indispensable in networking setups. This versatility allows RJ45 to connect devices like computers, routers, and switches seamlessly. Its durability and efficiency make it a networking staple. As network demands evolve, RJ45 remains a reliable choice for high-speed connections.
Shielding: UTP vs. STP Cables
Ethernet cables come in two main shielding types: UTP and STP. UTP stands for Unshielded Twisted Pair. These cables do not have additional shielding. They rely on twisted pairs to reduce interference. UTP cables are often cheaper and widely used in home networks.
STP, or Shielded Twisted Pair, adds a layer of protection. This extra shielding guards against electromagnetic interference. It makes STP cables ideal for industrial settings. STP cables are more suited for environments with heavy machinery or electrical noise.
Choosing between UTP and STP depends on the setting. UTP works well for low-interference areas. STP is better for high-interference environments. Each type serves distinct purposes, so consider your network’s specific needs. Consider also the costs and installation challenges associated with STP cables.
TIA/EIA Standards and Cable Lengths
When selecting Ethernet cables, standards are crucial. The TIA/EIA standards ensure compatibility and performance. They set guidelines for everything from wiring to materials. These standards help maintain network integrity. Compliance is essential for reliable networking.
The TIA/EIA standards also address cable lengths. Longer cables can cause signal loss. Typically, Ethernet cables should not exceed 100 meters. This limit maintains data speed and reduces latency. Shorter cables can sometimes improve performance.
Understanding these standards helps in network planning. Choosing cables within the proper length is key. It ensures the efficient and effective operation of your network. Adhering to these guidelines prevents potential connectivity issues. Always check that your cables meet TIA/EIA standards for the best network experience.
Patch Cables and Crossover Cables: Use Cases
Patch cables are common in connecting devices to network infrastructure. They typically link computers to network switches or routers. These cables are versatile and often used in office and home setups.
Crossover cables have a specific purpose. They connect similar devices directly, such as two computers. This is achieved by crossing the send and receive wires, facilitating direct communication.
Understanding when to use each cable type is essential. Patch cables are for connecting to a network, while crossover cables directly link devices. Choosing the correct cable ensures smooth data transmission and optimal performance.
Plenum-rated vs. PVC Cables
When selecting Ethernet cables, material matters. Plenum-rated cables are designed for spaces with air circulation. They meet strict fire safety standards, emitting less smoke if burned.
PVC cables are more common and budget-friendly. They are suitable for standard installations but don't offer the same fire resistance as plenum-rated options. Choosing between them depends on your installation environment and safety needs. Opt for plenum cables in air-handling spaces like ceilings, and choose PVC for cost-effective, ordinary installations. Always prioritize safety and compliance with local building codes.
Bandwidth and Data Speed: What You Need to Know?
Bandwidth and data speed are crucial to network performance. Bandwidth refers to the maximum data transfer capacity of a network. It's measured in megabits per second (Mbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps).
Ethernet cable categories determine bandwidth capacity. Higher category cables, such as Cat6 or Cat8, support faster data speeds. This means quicker downloads and smoother streaming experiences. For example, Cat5e cables offer up to 1 Gbps, while Cat6a can handle 10 Gbps.
Choosing the right Ethernet cable impacts your network's efficiency. Ensure your cable matches your internet speed capabilities. As internet speeds and data demands rise, consider higher-category cables. Investing in better bandwidth today could save you from future upgrades and keep your network running seamlessly.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) Explained
Power over Ethernet (PoE) allows electrical power and data to travel over a single Ethernet cable. This simplifies the installation of devices by eliminating the need for separate power cords. PoE is particularly useful for devices like IP cameras, wireless access points, and VoIP phones where electrical outlets are scarce.
PoE technology varies in power levels, ranging from 15 watts to more than 90 watts. Choosing the right PoE-capable switch or injector depends on your device's power needs. Deploying PoE simplifies both cabling and electrical planning, making networks more efficient and cleaner.
Cable Management and Installation Tips
Proper cable management is essential for maintaining an efficient and reliable network. Organized cables reduce clutter and make troubleshooting easier. Using cable trays, ties, and labels helps keep cables neat and identifiable.
When planning an installation, consider the length and type of cable required for your setup. Keeping cable runs within recommended lengths prevents signal loss and maintains network performance. Ensure that cables are installed away from potential sources of interference, like power lines and fluorescent lights.
Avoid sharp bends and kinks in cables as these can damage wires and degrade performance. Carefully route cables to maintain a smooth flow, respecting the cable's bend radius. Regularly check and maintain your cables to ensure sustained network health and avoid unexpected disruptions.
Future-Proofing Your Network with Ethernet Cables
Investing in the right Ethernet cables today can prepare your network for tomorrow's demands. Selecting higher-category cables, such as Cat6a or Cat8, increases bandwidth and speed capabilities, ready for future upgrades. These cables support higher data rates, making them suitable for emerging technologies.
Consider the potential growth of connected devices in your network. More devices mean higher data flow, requiring robust infrastructure. A future-proofed network accommodates increased traffic without compromising performance or stability.
Planning for scalability ensures your network can adapt to evolving needs. Evaluate your network layout for flexibility and expansion opportunities. By choosing quality cabling and efficient routing, your infrastructure remains agile and efficient for years to come.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Network
Choosing the right Ethernet cable requires understanding your network's current and future needs. Consider factors like speed requirements, layout, and potential expansions. By selecting the appropriate category, you ensure performance and reliability.
Stay informed about technological advancements and standards in networking. This knowledge helps you make informed decisions and keeps your network efficient. Investing in quality Ethernet cables is a wise move to support your network's growth and adaptability.


 ADSS Fiber Optic Cable
ADSS Fiber Optic Cable ASU Fiber Optic Cable
ASU Fiber Optic Cable OPGW Fiber Optic Cable
OPGW Fiber Optic Cable FTTH Fiber Optic Cable
FTTH Fiber Optic Cable Figure 8 Fiber Optic Cable
Figure 8 Fiber Optic Cable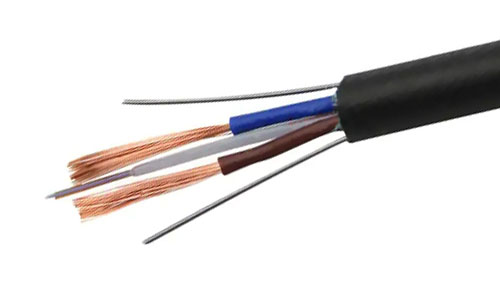 Photoelectric Composite Fiber Optic Cable
Photoelectric Composite Fiber Optic Cable Underground & Pipeline Fiber Optic Cable
Underground & Pipeline Fiber Optic Cable Air-Blown Micro Fiber Optic Cable
Air-Blown Micro Fiber Optic Cable Indoor Fiber Optic Cable
Indoor Fiber Optic Cable Fiber Optic Distribution Box
Fiber Optic Distribution Box Multiport Service Termina Box
Multiport Service Termina Box Fiber Optical Terminal Box
Fiber Optical Terminal Box Fiber Optic Splice Closure
Fiber Optic Splice Closure Fiber Optic Clamps
Fiber Optic Clamps Fiber Optic Cable Fittings
Fiber Optic Cable Fittings ADSS Fiber Cable
ADSS Fiber Cable ASU Fiber Cable
ASU Fiber Cable OPGW Fiber Cable
OPGW Fiber Cable FTTH Fiber Cable
FTTH Fiber Cable Figure 8 Fiber Cable
Figure 8 Fiber Cable Photoelectric Composite Fiber Cable
Photoelectric Composite Fiber Cable Underground & Pipeline Fiber Cable
Underground & Pipeline Fiber Cable Air-Blown Micro Fiber Cable
Air-Blown Micro Fiber Cable Aerial Fiber Cable
Aerial Fiber Cable Indoor Fiber Cable
Indoor Fiber Cable Fiber Optical Terminal Box
Fiber Optical Terminal Box Fiber Optic Distribution Box
Fiber Optic Distribution Box Multiport Service Termina Box
Multiport Service Termina Box Fiber Optic Clamps
Fiber Optic Clamps About Us
About Us Our Team
Our Team History
History R&D Strength
R&D Strength Production Base
Production Base Warehouse & Logistics
Warehouse & Logistics Quality
Quality FAQs
FAQs