How do Fiber Optic Cables Work?
Contact us for more sample,According to your needs, customize for you
inquiry nowHow do Fiber Optic Cables Work?
Fiber optic cables work by transmitting data as pulses of light through a strand of glass or plastic fiber. Here's a basic overview of how they function:
Light Transmission: A fiber optic cable consists of a core, which is the thin glass or plastic strand through which light travels, surrounded by a cladding layer that reflects light back into the core, preventing signal loss. The core and cladding have different refractive indices, allowing for total internal reflection to occur.
Light Source: At one end of the fiber optic cable, there's a light source, usually a laser or an LED (Light Emitting Diode). This light source generates light signals that are transmitted into the fiber optic cable.
Propagation: The light signals enter the core of the fiber optic cable and travel along its length through a process called total internal reflection. Essentially, the light bounces off the cladding layer, continuously reflecting back into the core.
Signal Reception: At the other end of the fiber optic cable, there's a receiver that detects the light signals. This receiver typically contains a photodiode or a photodetector that converts the light signals into electrical signals.
Data Transmission: The electrical signals obtained from the photodiode are then processed and converted back into digital data, which can be understood by electronic devices such as computers, routers, or phones.
Sure! Below is The Structure of an Optical Fiber Diagram:
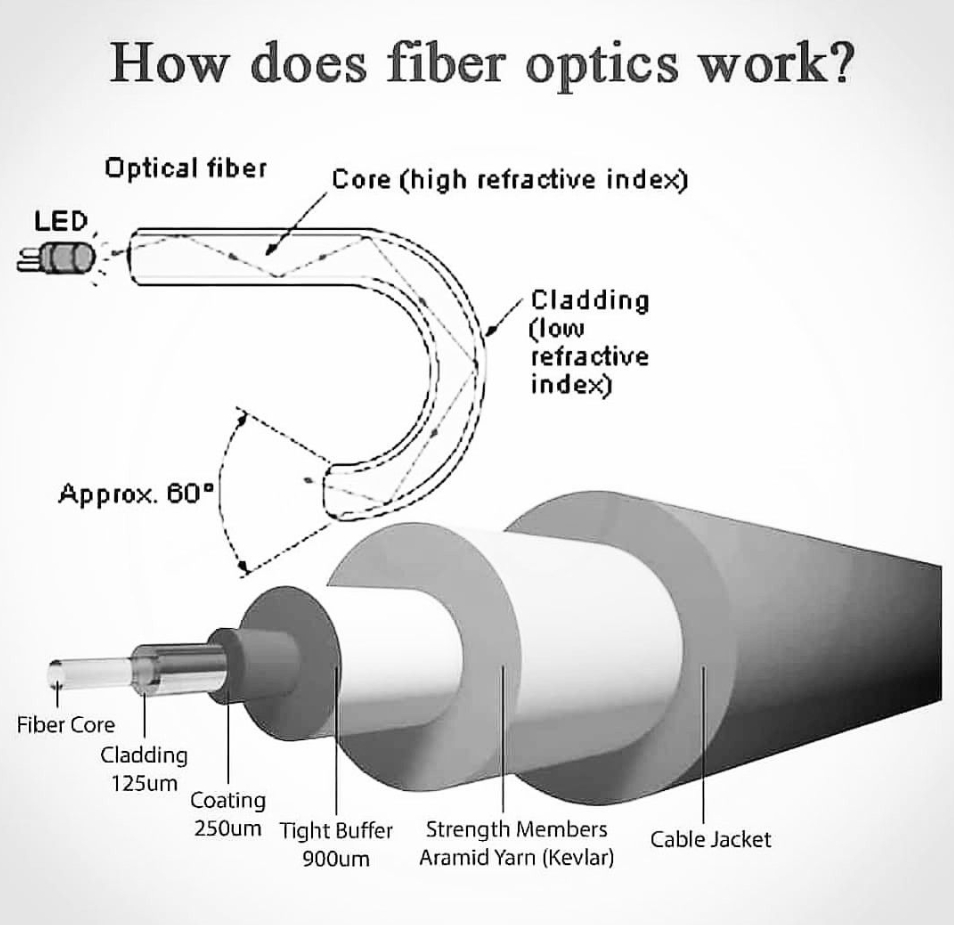
Core: The core is the central part of the optical fiber through which light travels. It is typically made of glass or plastic and has a higher refractive index than the cladding, allowing light to be guided along the fiber through total internal reflection.
Cladding: The cladding surrounds the core and is made of a material with a lower refractive index than the core. Its purpose is to reflect light back into the core, preventing signal loss and maintaining the integrity of the light signal as it travels through the fiber.
Buffer Coating: In practical optical fiber cables, there's often an additional layer called a buffer coating surrounding the cladding. This coating provides protection to the fiber from external factors such as moisture, physical damage, and temperature changes.
This basic diagram illustrates the fundamental structure of an optical fiber, but in practical applications, optical fibers are bundled together within protective jackets to form fiber optic cables used for telecommunications, internet transmission, and various other applications.
Fiber optic cables offer several advantages over traditional copper cables, including higher bandwidth, faster data transmission rates, immunity to electromagnetic interference, and greater security due to the difficulty of tapping into the signal without disrupting it. These characteristics make fiber optic cables the preferred choice for long-distance telecommunications and high-speed internet connections.


 ADSS Fiber Optic Cable
ADSS Fiber Optic Cable ASU Fiber Optic Cable
ASU Fiber Optic Cable OPGW Fiber Optic Cable
OPGW Fiber Optic Cable FTTH Fiber Optic Cable
FTTH Fiber Optic Cable Figure 8 Fiber Optic Cable
Figure 8 Fiber Optic Cable Photoelectric Composite Fiber Optic Cable
Photoelectric Composite Fiber Optic Cable Underground & Pipeline Fiber Optic Cable
Underground & Pipeline Fiber Optic Cable Air-Blown Micro Fiber Optic Cable
Air-Blown Micro Fiber Optic Cable Indoor Fiber Optic Cable
Indoor Fiber Optic Cable Fiber Optic Distribution Box
Fiber Optic Distribution Box Multiport Service Termina Box
Multiport Service Termina Box Fiber Optical Terminal Box
Fiber Optical Terminal Box Fiber Optic Splice Closure
Fiber Optic Splice Closure Fiber Optic Clamps
Fiber Optic Clamps Fiber Optic Cable Fittings
Fiber Optic Cable Fittings ADSS Fiber Cable
ADSS Fiber Cable ASU Fiber Cable
ASU Fiber Cable OPGW Fiber Cable
OPGW Fiber Cable FTTH Fiber Cable
FTTH Fiber Cable Figure 8 Fiber Cable
Figure 8 Fiber Cable Photoelectric Composite Fiber Cable
Photoelectric Composite Fiber Cable Underground & Pipeline Fiber Cable
Underground & Pipeline Fiber Cable Air-Blown Micro Fiber Cable
Air-Blown Micro Fiber Cable Aerial Fiber Cable
Aerial Fiber Cable Indoor Fiber Cable
Indoor Fiber Cable Fiber Optical Terminal Box
Fiber Optical Terminal Box Fiber Optic Distribution Box
Fiber Optic Distribution Box Multiport Service Termina Box
Multiport Service Termina Box Fiber Optic Clamps
Fiber Optic Clamps About Us
About Us Our Team
Our Team History
History R&D Strength
R&D Strength Production Base
Production Base Warehouse & Logistics
Warehouse & Logistics Quality
Quality FAQs
FAQs