What is Optical Splitter?
ontact us for more sample,According to your needs, customize for you
inquiry nowWhat is Optical Splitter?
An optical splitter, also known as a fiber optic splitter or fiber splitter, is a passive optical device used in fiber-optic networks to split an optical signal into multiple paths. These devices are crucial for distributing optical signals to multiple destinations without the need for additional active components like amplifiers or repeaters.
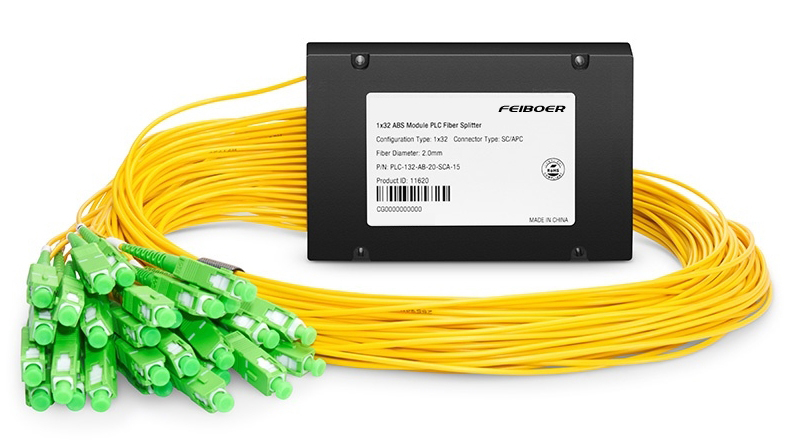

Here's how an optical splitter typically works:
Passive Operation: Optical splitters do not require external power sources; they operate passively, relying solely on the properties of light propagation within optical fibers.
Dividing Optical Signals: When an optical signal enters an optical splitter through its input port, the splitter divides the signal into two or more output ports. The splitting ratio determines how the input signal is distributed among the output ports.
Splitting Ratio: Optical splitters can have various splitting ratios, such as 1:2, 1:4, 1:8, 1:16, etc. For example, a 1:4 splitter divides the input signal into four equal parts, sending one-fourth of the signal to each output port.
Waveguide Technology: Most optical splitters use waveguide technology to divide the optical signal. Waveguides are structures within the splitter that guide the light along specific paths, allowing for precise splitting of the signal.
Applications: Optical splitters are commonly used in passive optical networks (PONs), which are widely used for telecommunications and broadband internet services. They allow a single optical fiber to serve multiple users or locations, reducing the amount of fiber needed in the network and lowering deployment costs.
Types of Splitters: There are various types of optical splitters, including fused fiber splitters, planar lightwave circuit (PLC) splitters, and micro-optic splitters. Each type has its advantages and is used in different network configurations based on factors such as splitting ratio, wavelength compatibility, and cost.
Overall, optical splitters play a crucial role in the efficient distribution of optical signals in fiber-optic communication networks, enabling the delivery of high-speed internet, television, and other services to multiple users or locations.
An optical splitter works by using passive optical components to divide an incoming optical signal into multiple output signals, which can then be routed to different destinations.
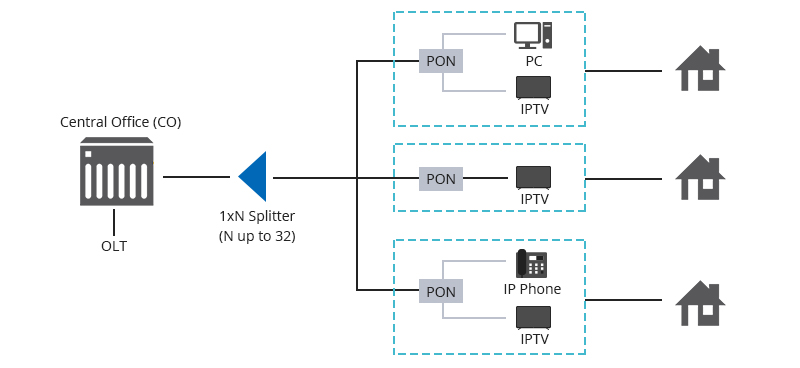
Here's a more detailed explanation of how optical splitters work:
Input Signal: The optical splitter receives an incoming optical signal through its input port. This signal typically originates from a single optical source, such as an optical transmitter.
Splitting Process: Once the optical signal enters the splitter, it encounters a splitting mechanism, which can vary depending on the type of splitter. The most common types of splitters are based on either fused fiber technology or planar lightwave circuit (PLC) technology.
Fused Fiber Splitters: In fused fiber splitters, the incoming optical signal is split using a technique where multiple fibers are fused together at a microscopic level. Light entering the input fiber is distributed across the fused region, causing it to be divided among the output fibers based on the splitter's design and splitting ratio.
PLC Splitters: Planar lightwave circuit splitters utilize a flat waveguide chip to split the optical signal. The chip contains a network of waveguides that divide the signal optically without physically altering the fibers. Light entering the input waveguide is distributed among the output waveguides based on the splitter's design.
Output Signals: As a result of the splitting process, the incoming optical signal is divided into multiple output signals, each traveling through a separate output port of the splitter. The number of output ports and the splitting ratio determine how the signal is distributed among the output channels.
Passive Operation: Optical splitters are passive devices, meaning they do not require external power sources to operate. They rely on the properties of light propagation within optical fibers and the design of the splitter components to split the signal effectively.
Losses and Efficiency: While optical splitters are highly efficient devices, they do introduce some signal loss due to the splitting process. The splitting ratio, quality of splitter components, and insertion loss characteristics determine the overall efficiency of the splitter.
Overall, optical splitters play a crucial role in enabling the efficient distribution of optical signals in fiber-optic communication networks, allowing a single optical source to serve multiple users or destinations simultaneously.


 ADSS Fiber Optic Cable
ADSS Fiber Optic Cable ASU Fiber Optic Cable
ASU Fiber Optic Cable OPGW Fiber Optic Cable
OPGW Fiber Optic Cable FTTH Fiber Optic Cable
FTTH Fiber Optic Cable Figure 8 Fiber Optic Cable
Figure 8 Fiber Optic Cable Photoelectric Composite Fiber Optic Cable
Photoelectric Composite Fiber Optic Cable Underground & Pipeline Fiber Optic Cable
Underground & Pipeline Fiber Optic Cable Air-Blown Micro Fiber Optic Cable
Air-Blown Micro Fiber Optic Cable Indoor Fiber Optic Cable
Indoor Fiber Optic Cable Fiber Optic Distribution Box
Fiber Optic Distribution Box Multiport Service Termina Box
Multiport Service Termina Box Fiber Optical Terminal Box
Fiber Optical Terminal Box Fiber Optic Splice Closure
Fiber Optic Splice Closure Fiber Optic Clamps
Fiber Optic Clamps Fiber Optic Cable Fittings
Fiber Optic Cable Fittings ADSS Fiber Cable
ADSS Fiber Cable ASU Fiber Cable
ASU Fiber Cable OPGW Fiber Cable
OPGW Fiber Cable FTTH Fiber Cable
FTTH Fiber Cable Figure 8 Fiber Cable
Figure 8 Fiber Cable Photoelectric Composite Fiber Cable
Photoelectric Composite Fiber Cable Underground & Pipeline Fiber Cable
Underground & Pipeline Fiber Cable Air-Blown Micro Fiber Cable
Air-Blown Micro Fiber Cable Aerial Fiber Cable
Aerial Fiber Cable Indoor Fiber Cable
Indoor Fiber Cable Fiber Optical Terminal Box
Fiber Optical Terminal Box Fiber Optic Distribution Box
Fiber Optic Distribution Box Multiport Service Termina Box
Multiport Service Termina Box Fiber Optic Clamps
Fiber Optic Clamps About Us
About Us Our Team
Our Team History
History R&D Strength
R&D Strength Production Base
Production Base Warehouse & Logistics
Warehouse & Logistics Quality
Quality FAQs
FAQs